| XC3000 | XC4000E | XC4000X | XC5200 | XC9000 | Spartan | SpartanXL | Virtex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macro | Macro | Macro | Macro | Macro | Macro | Macro | Macro |
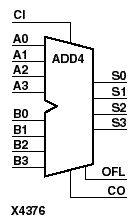
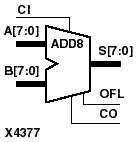
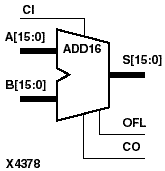
ADD4, ADD8, and ADD16 add two words and a carry-in (CI), producing a sum output and carry-out (CO) or overflow (OFL). ADD4 adds A3 - A0, B3 - B0, and CI producing the sum output S3 - S0 and CO (or OFL). ADD8 adds A7 - A0, B7 - B0, and CI, producing the sum output S7 - S0 and CO (or OFL). ADD16 adds A15 - A0, B15 - B0 and CI, producing the sum output S15 - S0 and CO (or OFL).
ADD4, ADD8, and ADD16 are implemented in the XC4000 and Spartans using carry logic and relative location constraints, which assure most efficient logic placement.
ADD4, ADD8, ADD16 can operate on either 4-, 8-, 16-bit unsigned binary numbers or 4-, 8-, 16-bit twos-complement numbers, respectively. If the inputs are interpreted as unsigned binary, the result can be interpreted as unsigned binary. If the inputs are interpreted as twos complement, the output can be interpreted as twos complement. The only functional difference between an unsigned binary operation and a twos-complement operation is how they determine when “overflow” occurs. Unsigned binary uses CO, while twos-complement uses OFL to determine when “overflow” occurs.
For unsigned binary operation, ADD4 can represent numbers between 0 and 15, inclusive; ADD8 between 0 and 255, inclusive; ADD16 between 0 and 65535, inclusive. CO is active (High) when the sum exceeds the bounds of the adder.
OFL is ignored in unsigned binary operation.
For twos-complement operation, ADD4 can represent numbers between -8 and +7, inclusive; ADD8 between -128 and +127, inclusive; ADD16 between -32768 and +32767, inclusive. OFL is active (High) when the sum exceeds the bounds of the adder.
CO is ignored in twos-complement operation.
This is the ADD4 (4-bit), ADD8 (8-bit), and ADD16 (16-bit) topology for XC4000 and Spartan series devices.
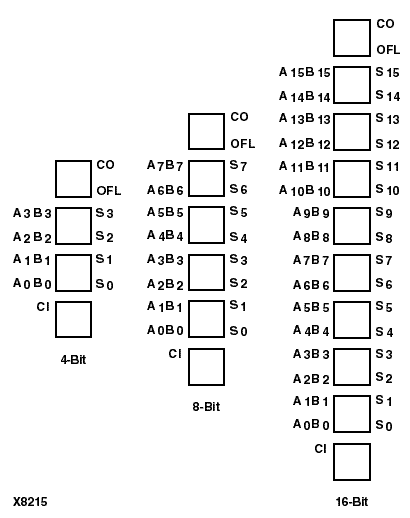
This is the ADD8 (8-bit) and ADD16 (16-bit) topology for XC5200 devices.
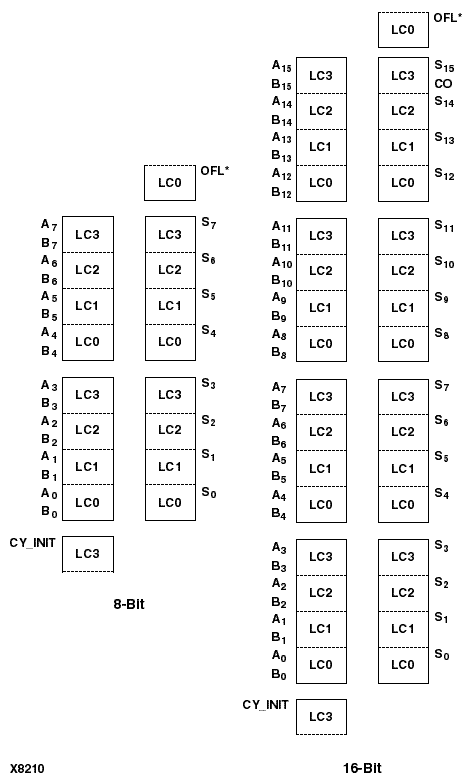
Figure 3.9 ADD8 Implementation XC3000 |
Figure 3.10 ADD8 Implementation XC4000, Spartans |
Figure 3.11 ADD8 Implementation XC5200 |
Figure 3.12 ADD8 Implementation Virtex |
Figure 3.13 ADD4 Implementation XC9000 |
Figure 3.14 ADD8 Implementation XC9000 |