| Element | XC3000 | XC4000E | XC4000X | XC5200 | XC9000 | Spartan | SpartanXL | Virtex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFDX | N/A | Primitive | Primitive | N/A | N/A | Primitive | Primitive | Macro |
| IFDX4, IFDX8, IFDX16 | N/A | Macro | Macro | N/A | N/A | Macro | Macro | Macro |
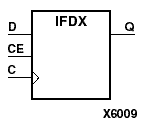
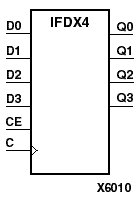
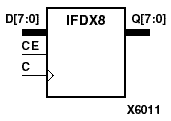
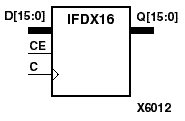
The IFDX D-type flip-flop is contained in an input/output block (IOB). The input (D) of the flip-flop is connected to an IPAD or an IOPAD (without using an IBUF). The D input provides data input for the flip-flop, which synchronizes data entering the chip. The data on input D is loaded into the flip-flop during the Low-to-High clock (C) transition and appears at the output (Q). The clock input can be driven by internal logic or through another external pin. When CE is Low, flip-flop outputs do not change.
The flip-flops are asynchronously cleared with Low outputs when power is applied. FPGAs simulate power-on when global set/reset (GSR) is active. GSR (XC4000, Spartans) default to active-High but can be inverted by adding an inverter in front of the GSR input of the STARTUP symbol.
For information on legal IFDX, IFDX_1, ILDX, and ILDX_1 combinations, refer to the “ILDX, 4, 8, 16” section.
| Inputs | Outputs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | Dn | C | Qn |
| 1 | Dn | dn | |
| 0 | X | X | No Chg |
| dn = state of referenced input (Dn) one setup time prior to active clock transition | |||
Figure 6.14 IFDX Implementation Virtex |
Figure 6.15 IFDX8 Implementation XC4000, Spartans, Virtex |